
一、Spring JDBC
1、Spring JdbcTemplate的解析
针对数据库的操作,Spring框架提供了JdbcTemplate类,该类是Spring框架数据抽象层的基础,其他更高层次的抽象类却是构建于JdbcTemplate类之上。可以说,JdbcTemplate类是Spring JDBC的核心类。
JdbcTemplate类的继承关系十分简单,它继承自抽象类JdbcAccessor,同时实现了JdbcOperations接口,如下图所示:
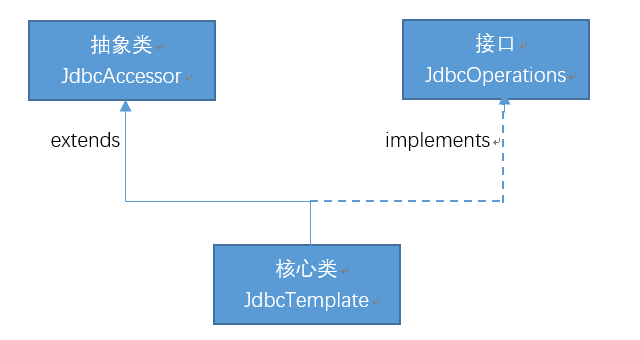
从图可以看出,JdbcTemplate 类的直接父类是JdbcAccessor,该类为子类提供了一些访问数据库时使用的公共属性,具体如下:
- DataSource:其主要功能是获取数据库连接,具体实现时还可以引入对数据库连接的缓冲池和分布式事务的支持,它可以作为访问数据库资源的标准接口。
- SQLExceptionTranslator:org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLExceptionTranslator接口负责对SQLException进行转译工作。通过必要的设置或者获取SQLExceptionTranslator中的方法,可以使J大白菜Template 在需要处理SQLException时,委托SQLExceptionTranslator的实现类来完成相关的转译工作。
JdbcOperations 接口定义了在JdbcTemplate类中可以使用的操作集合,包括添加、修改、查询和删除等操作。
2.SpringJDBC 的配置
Spring JDBC 模块由4个包组成,分别是core(核心包)、dataSource(数据源包)、object(对象包)和support(支持包),其说明如下表所示:
| 包名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| core | 包含了JDBC的核心功能,包括JdbcTemplate类、SimpleJDBCInsert类、SimpleJDBCCall类以及 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate类 |
| dataSource | 访问数据源的实用工具类,它有多种数据源的实现,可以在JavaEE容器外部测试JDBC代码 |
| object | 以面向对象的方式访问数据库,它允许执行查询并将返回结果作为业务对象,可以在数据表的列和业务对象的属性之间映射查询结果 |
| support | 包含了core 和 object包的支持类,例如,提供异常转换功能的SQLException类 |
从表可以看出,Spring 对数据库的操作都封装在了这几个包中,而想要使用Spring JDBC,就需要对其进行配置。在Spring中,JDBC的配置是在配置文件applicationContext.xml中完成的,其配置模板如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1.配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<!-- 数据库驱动 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<!-- 连接数据库的url -->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"/>
<!-- 连接数据库的用户名 -->
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<!-- 连接数据库的密码 -->
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- 2.配置JDBC模板 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 默认必须使用数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 3.配置注入类 -->
<bean id="xxx" class="xxx">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>
</bean>
...
</beans>
上述代码中,定义了3个Bean,分别是dataSource、jdbcTemplate 和需要注入类的Bean。其中dataSource对应的org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource类用于对数据源进行配置,jdbcTemplate 对应的 org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate类中定义了JdbcTemplate的相关配置。上述代码中dataSource的配置就是JDBC连接数据库时所需的4个属性。如下表所示:
| 属性名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| driverClassName | 所使用的驱动名称,对应驱动JAR包中的Driver类 |
| url | 数据源所在地址 |
| username | 访问数据库的用户名 |
| password | 访问数据库的密码 |
表中的4个属性,需要根据数据库类型或者机器配置的不同设置相应的属性值。例如,如果数据库类型不同,需要更改驱动名称;如果数据库不再本地,则需要将地址中的localhost地换成相应的ip地址;如果修改过MySQL 数据库的端口号(默认3306),则需要加上修改后的端口号,如果未修改,则端口号可以省略;同时连接数据库的用户名和密码需要与数据库创建时设置的用户名与密码保持一致。
定义JdbcTemplate时,需要将dataSource注入到JdbcTemplate中,而其他需要使用JdbcTemplate的Bean,也需要将JdbcTemplate注入到该Bean中(通常注入到Dao类中,在Dao类中进行与数据库的相关操作)。
二、Spring JdbcTemplate 的常用方法
1.execute()
execute(String sql) 方法能够完成执行SQL语句的功能。下面以创建数据表SQL语句为例,具体步骤如下:
(1)在MySQL 中,创建一个名为spring 的数据库,创建方式如下图所示:
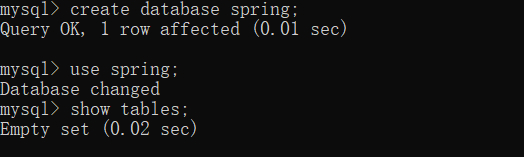
create database spring;
use spring;
show tables;
(2)在Eclipse中,创建一个新的Web项目,将运行Spring框架所需的5个基础包、MySQL数据库的驱动JAR包、SpringJDBC 的JAR包以及Spring事务处理的JAR包复制到项目的lib目录,包如下图所示:

(3)在src目录下,创建配置文件applicationContext.xml,在该文件中配置id为dataSource的数据源Bean和id为jdbcTemplate的JDBC模板Bean,并将数据源注入到JDBC模板中,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1.配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<!-- 数据库驱动 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<!-- 连接数据库的url -->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost/spring"/>
<!-- 连接数据库的用户名 -->
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<!-- 连接数据库的密码 -->
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
<!-- 2.配置JDBC模板 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 默认必须使用数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
(4)在src目录下,创建一个com.cn.jdbc包,在该包中创建测试类JdbcTemplateTest。在该类main方法中通过Spring容器获取在配置文件中定义的JdbcTemplate实例,然后使用该实例的execute(String sql)方法执行创建数据表的SQL语句,代码如下:
package com.cn.jdbc;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext appt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取JdbcTemplate实例
JdbcTemplate jdTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) appt.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//使用execute()方法执行SQL语句,创建用户账户管理表account
jdTemplate.execute("create table account("+"id int primary key auto_increment,"+
"username varchar(50),"+"balance double)");
System.out.println("账户表account创建成功!");
}
}
成功运行程序后,再次查询spring数据库,结果如下图所示:
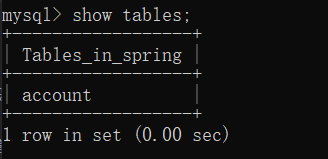
程序使用execute(String sql)方法执行的SQL语句成功创建了数据表account。
2.update()
update()方法可以完成插入、更新和删除数据的操作。在JdbcTemplate类中,提供了一系列的update()方法,常用方法如下表:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int update(String sql) | 该方法是最简单的update方法重载形式,它直接执行传入的SQL语句,并返回受影响的行数 |
| int update(PreparedStatementCreator psc | 该方法执行从PreparedStatementCreator 返回的语句,然后返回首先影响的行数 |
| int update(String sql,PreparedStatementSetter pss) | 该方法通过PreparedStatementSetter 设置SQL语句中的参数,并返回受影响的行数 |
| int update(String sql,Object ... args) | 该方法使用Object...设置SQL语句中的参数,要求参数补鞥哪位NULL,并返回受影响的行数 |
通过一个用户管理的例子来演示update()方法的使用,步骤如下:
(1)在com.cn.jdbc 包中,创建Account类,在该类中定义 id、username 和 balance 属性,以及其对应的 getter/setter方法,如下所示:
package com.cn.jdbc;
public class Account {
private Integer id; //账户id
private String username; //用户名
private Double balance; //用户余额
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", balance=" + balance + "]";
}
}
(2)在com.cn.jdbc包中,创建接口AccountDao,并在接口中定义添加、更新和删除账户的方法,代码如下:
package com.cn.jdbc;
public interface AccountDao {
//添加
public int addAccount(Account account);
//更新
public int updateAccount(Account account);
//删除
public int deleteAccount(int id);
}
(3)在com.cn.jdbc包中,创建AccountDao接口的实现类AccountDaoImpl,并在类中实现添加、更新和删除账户的方法,代码如下:
package com.cn.jdbc;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
//声明JdbcTemplate属性及其setter方法
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
//添加账户
@Override
public int addAccount(Account account) {
//定义SQL
String sql = "insert into account(username,balance) value(?,?)";
//定义数组来存储SQL语句中的参数
Object [] obj = new Object[] {
account.getUsername(),
account.getBalance()
};
//实行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数
int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql,obj);
return num;
}
//更新账户
@Override
public int updateAccount(Account account) {
//定义SQL
String sql = "update account set username=?,balance=? where id=?";
//定义数组来存储SQL语句中的参数
Object[] params = new Object[] {
account.getUsername(),
account.getBalance(),
account.getId()
};
//实行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数
int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql,params);
return num;
}
//删除账户
@Override
public int deleteAccount(int id) {
//定义SQL
String sql = "delete from account where id = ?";
//执行删除操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数
int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
return num;
}
}
(4)在applicationContext.xml中,定义一个id为accountDao的Bean,该Bean用于将jdbcTemplate注入到accountDao实例中,代码如下:
<!-- 定义id为accountDao的Bean -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.cn.jdbc.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 将jdbcTemplate注入到accountDao实例中 -->
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>
</bean>
(5)在测试类JdbcTemplateTest中,添加一个测试方法addAccountTest(),该方法主要用于添加用户账户信息,代码如下:
@Test
public void addAccountTest() {
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext appc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取AccountDao实例
AccountDao accountDao = appc.getBean("accountDao",AccountDao.class);
//创建Account对象,并向Account对象中添加数据
Account account = new Account();
account.setUsername("Mike");
account.setBalance(1024.00);
//执行addAccount()方法,并获取返回结果
int num = accountDao.addAccount(account);
if(num>0) {
System.out.println("成功插入了"+num+"条数据!");
}
else {
System.out.println("插入操作执行失败!");
}
}
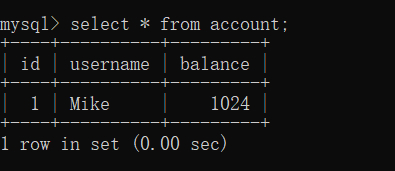
运行结果如下:

查询数据库结果如下:
(6)执行完插入操作后,接下来使用JdbcTemplate类的update()方法执行更新操作。在测试类JdbcTemplateTest中,添加一个测试方法updateAccountTest(),代码如下:
@Test
public void updateAccountTest() {
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext appc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取AccountDao实例
AccountDao accountDao = appc.getBean("accountDao",AccountDao.class);
//创建Account对象,并向Account对象中添加数据
Account account = new Account();
account.setId(1);
account.setUsername("Lili");
account.setBalance(2048.00);
//执行addAccount()方法,并获取返回结果
int num = accountDao.addAccount(account);
if(num>0) {
System.out.println("成功修改了"+num+"条数据!");
}
else {
System.out.println("修改操作执行失败!");
}
}
运行结果如下:

再次查询数据表如下所示:
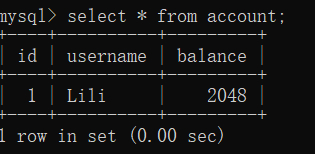
(7)在测试类JdbcTemplateTest 中,添加一个测试方法deleteAccountTest(),来执行删除操作,代码如下:
@Test
public void deleteAccountTest() {
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext appc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取AccountDao实例
AccountDao accountDao = appc.getBean("accountDao",AccountDao.class);
//执行deleteAccount()方法,并获取返回结果
int num = accountDao.deleteAccount(1);
if(num>0) {
System.out.println("成功删除了"+num+"条数据!");
}
else {
System.out.println("删除操作执行失败!");
}
}
成功执行后查询数据表如图:
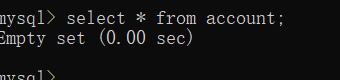
3.query()
JdbcTemplate类中还提供了了大量的query()方法来处理各种对数据库表的查询操作。其中几个常用的query()方法如下:
| col1 | col2 |
|---|---|
| List query(String sql,RowMapper rowMapper) | 执行String 类型参数提供的SQL语句,并通过RowMap普洱返回一个List类型的结果 |
| List query(String sql,PreparedStatementSetter pss,RowMapper rowMapper) | 根据String类型参数提供的SQL语句创建PreparedStatement对象,通过RowMap普洱将结果返回到List中 |
| List query(String sql,Object[] args,RowMapper rowMapper) | 使用Object[]的值来设置SQL语句中的参数值,采用RowMapper回调方法可以直接返回List类型的数据 |
| queryForObject(String sql,RowMapper rowMapper,Object... args) | 将args参数绑定到SQL语句中,并通过RowMapper返回一个Object 类型的单行记录 |
| queryForList(String sql,Object[] args,class | 该方法可以返回多行数据的结果,但必须是返回列表,elementType参数返回的是List元素类型 |
一个简单的示例案例步骤如下:
(1)向数据表account中插入几条数据,结果如下:
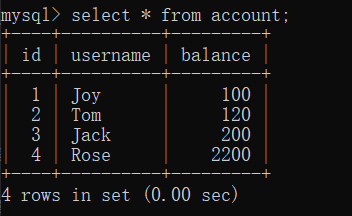
(2)在AccountDao中,分别创建一个通过id查询单个账户的查询所有账户的方法,代码如下:
//通过id查询
public Account findAccountById(int id);
//查询所有账户
public List<Account> findAllAccount();
(3)在AccountDao接口的实现类AccountDaoImpl中,实现接口中的方法,并使用query()方法分别进行查询,代码如下所示:
//通过id查询账户数据信息
public Account findAccountById(int id) {
//定义SQL语句
String sql = "select * from account where id = ?";
//创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象
RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class);
//将id绑定到SQL语句中,并通过RowMapper返回一个Object类型的单行记录
return this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper,id);
}
//查询所有账户信息
@Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
//定义SQL语句
String sql = "select * from account";
//创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象
RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class);
//执行静态的SQL查询,并通过RowMapper返回结果
return this.jdbcTemplate.query(sql,rowMapper);
}
上述代码中,BeanPropertyRowMapper 是 RowMapper接口的实现类,它可以自动地将数据表中的数据映射到用户自定义的类中(前提是用户自定义类中的字段要与数据表中的字段相对应)。创建完BeanPropertyRowMapper对象后,在findAccountById()方法中通过queryForObject()方法返回了一个Object类型的单行记录,而在findAllAccount()方法中通过query()方法返回了一个结果集合。
(4)在测试类JdbcTemplateTest中,添加一个测试方法findAccountByIdTest()来测试查询,代码如下:
@Test
public void findAccountByIdTest() {
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext appc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取AccountDao实例
AccountDao accountDao = appc.getBean("accountDao",AccountDao.class);
//执行findAccountById()方法
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
运行结果如下

(5)测试完条件查询单个数据的方法后,接下来测试查询所有用户账户信息的方法,在测试类JdbcTemplateTest中,添加一个测试方法findAllAccountTest(),代码如下:
@Test
public void findAllAccountTest() {
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext appc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取AccountDao实例
AccountDao accountDao = appc.getBean("accountDao",AccountDao.class);
//执行findAllAccount()方法,获取Account对象的集合
List<Account> account = accountDao.findAllAccount();
//循环输出集合中的对象
for (Account act : account) {
System.out.println(act);
}
}
运行结果如下所示:
